Nowadays, we hear about so many cyber-attacks and breaches on various systems in various organizations. As a result, it has become a top priority for companies to protect themselves from such attacks. Cyber-attacks can result in a loss of reputation and assets—consumer trust, credibility, company earnings, user data, etc. The list is endless.
So, to save themselves, many companies have devised a variety of strategies that they employ to protect their and their customer’s interests. Two methods of protection that have become a procedural necessity in these companies are simulation testing and penetration testing.
Let's start by taking a closer look at simulation and penetration testing.
What Are Breach and Attack Simulation?
Breach and attack simulation of cyber-attacks have become far too common in recent years. They’re a low-risk, continuous, and consistent way of testing that can show IT teams, business stakeholders, and other current flaws in a system.
Source
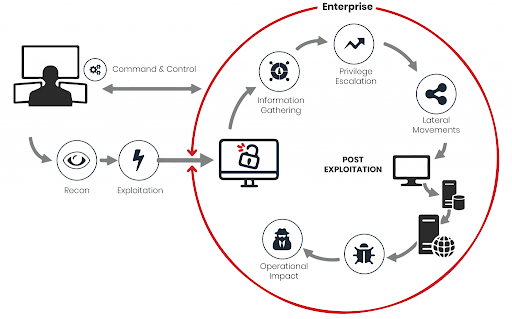
ABAS detects vulnerabilities by employing internal threats, data exfiltration, and lateral movement to test the strength of your system. It can work on specific data sets or methodologies to test specific vulnerabilities. Therefore, it employs unique test cases and actively seeks out vulnerabilities rather than merely satisfying and confirming that the system is free of flaws.
BAS is the outcome of combining "Red Team" and "Blue Team" pen testing and automating them on a regular basis. It can inject malware-like files onto your system to test if your system is vulnerable to detection. To carry out this type of attack, BAS can use the firewall or email to distribute malicious files.
As a result, it determines if the firewall and other security mechanisms in place are effective in protecting the organization from these threats. As a result of these factors, enterprises can determine how secure their network is and, if any vulnerabilities exist, how to address them.
What Is Penetration Testing?
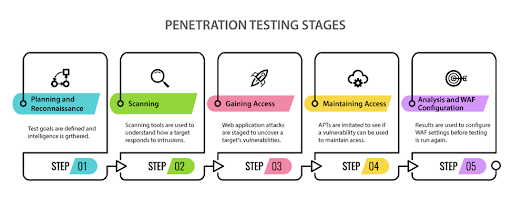
Penetration testing, often known as pen testing, is a security best practice that aims to improve an organization's architecture from a security standpoint. Internal security teams do penetration testing to secure the network and assets by identifying flaws in the system. Organizations require qualified professionals to complete these responsibilities. The main goal is to uncover system flaws that attackers can exploit to obtain access to sensitive information held by the company.
Source
Let us take an example to understand pen testing better. Assume that a business uses three separate servers, two of which have authentication enabled and the third server does not. An attacker can exploit this vulnerability and get unauthorized access to the organization's sensitive information.
To check for such vulnerabilities, qualified specialists such as ethical hackers are needed to save the organization and uncover the vulnerability before an attacker does. Pen testing is divided into stages—the tester obtains knowledge about the organization first and then looks for ways to exploit weaknesses in the system to gain access to the firm's systems and data.
Key Differences
| SNO | BAS | Pen Testing |
| 1 | Automated tools are used by these businesses to identify system vulnerabilities. | Penetration testers use manual testing to uncover vulnerabilities in an organization's assets. |
| 2 | It is a continuous strategy that operates 24 hours a day, seven days a week, 365 days a year. | Since it is a resource-intensive strategy, it is not carried out continuously. It only happens when the organization introduces a new asset or website. |
| 3 | It uses advanced persistent threats (APTs) to find malicious entities. | In pen testing, each tester has their own set of procedures for locating malicious entities or vulnerabilities. |
| 4 | The behavior-based detection of vulnerabilities in devices that exist in the organization is carried out through simulation. | Pen testing never performs behavioral detection in devices. |
| 5 | It automatically provides remediation steps to determine the severity. High severity remediation steps come first. | The remedial procedures in pen testing are based on the tester too. |
| 6 | It performs activities in a controlled environment to eliminate vulnerabilities before they reach the actual server. | Testers sometimes use payloads that can stop the processing of applications. |
| 7 | There is no need for extensive cybersecurity knowledge. | It may require a skilled tester. |
| 8 | Its processes work in the background so users are not aware of them. | The team may be aware that pen testing is being carried out as it generates a lot of traffic. |
| 9 | It can find the vulnerabilities and remediate them with the patch to be issued. | Testers only identify the vulnerability the developer needs to fix. Testers suggest ways to fix it. |
| 10 | It does not follow the conventional model of testing. It’s a new technology adopted by many organizations. | Pen testing has its own standard and approaches. |
| 11 | It is not as dependent on human skills. | It completely depends on human skill. |
| 12 | It increases efficiency and reduces the cost of testing. | Manual testing depends on the tester mindset and affects the output. Therefore, pen testing can vary from tester to tester. |
Conclusion
You require a skilled penetration tester with verified skills who can execute penetration testing in a timely manner. BAS, on the other hand, does not rely on human abilities. BAS is critical in protecting an organization's assets by simulating potential assaults and then delivering remedies based on the severity.
The benefit of BAS is that it is a continuous method, which means that it can test and provide solutions anytime changes occur in an organization. BAS examines everything from a security standpoint and allows you to halt the process if the implementation is not secure.